2.14.5. HTTP Service Configuration on Subordinate Nodes of a Virtuoso Cluster
This section applies to Virtuoso as of version 6.x and higher.
What
This documentation details how to configure the Subordinate (also called Slave) Nodes of a Virtuoso Elastic Cluster to service HTTP clients.
Why
By default, only the Primary (also called Master) instance of a Virtuoso Elastic Cluster is configured to provide HTTP services.
The Subordinate (also called Slave) nodes of the cluster may also be configured to provide HTTP services, enabling load balancing by spreading HTTP requests across the cluster's nodes.
How
This documentation details the steps for the installation and configuration of a Virtuoso Elastic Cluster on Unix:
-
Step 1
: Set up each instance as a HTTP Server;
-
Step 2
: Install and configure HTTP services on each instance;
-
Step 3
: Configure load balancing.
Set up each instance as an HTTP Server
Step 1 : Set up each instance as a HTTP Server
Each node can be configured to provide HTTP services as follows:
-
Copy the
[HTTP Server]section from the Primary instance's configuration file (by default,virtuoso.ini) to the configuration file of each Subordinate instance:[HTTPServer] ServerPort = 8890 ServerRoot = ../vsp DavRoot = DAV EnabledDavVSP = 0 HTTPProxyEnabled = 0 TempASPXDir = 0 DefaultMailServer = localhost:25 MaxClientConnections = 5 MaxKeepAlives = 10 KeepAliveTimeout = 10 MaxCachedProxyConnections = 10 ProxyConnectionCacheTimeout = 15 HTTPThreadSize = 280000 HttpPrintWarningsInOutput = 0 Charset = UTF-8 ;HTTPLogFile = logs/http.log MaintenancePage = atomic.html EnabledGzipContent = 1
-
Edit the
ServerPortparameter to make it unique on the machine hosting this instance; i.e., if a subordinate instance is running on same physical node as the primary instance, then the subordinate's HTTP port must to be changed (from 8890, for instance) to a unique port (e.g., 8891). -
Install the Virtuoso Conductor to enable HTTP Administration of the instance being configured. Note: if the subordinate instance is not on the same machine as the primary instance, then the vad directory may also need to be copied from the primary instance to the subordinate instance.:
SQL> vad_install ('../vad/conductor_dav.vad', 0); SQL_STATE SQL_MESSAGE VARCHAR VARCHAR _______________________________________________________________________________ 00000 No errors detected 00000 Installation of "Virtuoso Conductor" is complete. 00000 Now making a final checkpoint. 00000 Final checkpoint is made. 00000 SUCCESS 6 Rows. -- 10263 msec. SQL>
Install and configure HTTP services on each instance
Step 2 : Install and configure HTTP services on each instance
Any HTTP services required on the subordinate instance will need to specifically installed or configured on
that physical node. For example, the Virtuoso default SPARQL endpoint (/sparql
) may be configured by:
-
Log in into the Virtuoso Conductor http://hostname:port/conductor :
Figure 2.185. Configure SPARQL Endpoint: log in
-
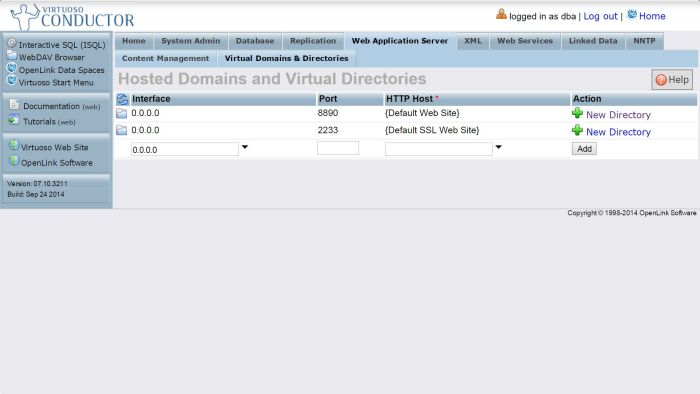
Go the the Web Application Server -> Virtual Domains & Directories tab:
Figure 2.186. Configure SPARQL Endpoint: Virtual Domains and Directories
-
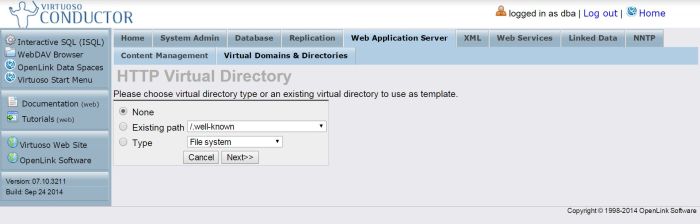
Select the New Directory Action for the Default Web Site HTTP host:
Figure 2.187. Configure SPARQL Endpoint: new directory
-
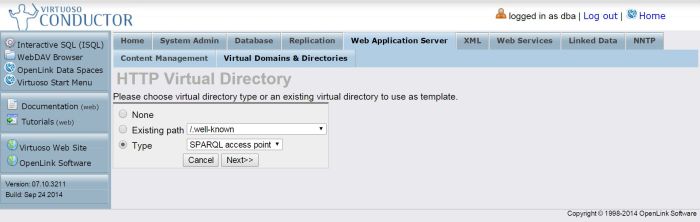
Select the Type radio button and SPARQL access point item from the drop down list box:
Figure 2.188. Configure SPARQL Endpoint: set type SPARQL
-
Click "Next".
-
Enter /sparql as the Path param in the Virtual Directory Information section and click Save Changes:
Figure 2.189. Configure SPARQL Endpoint: set /sparql virtual directory
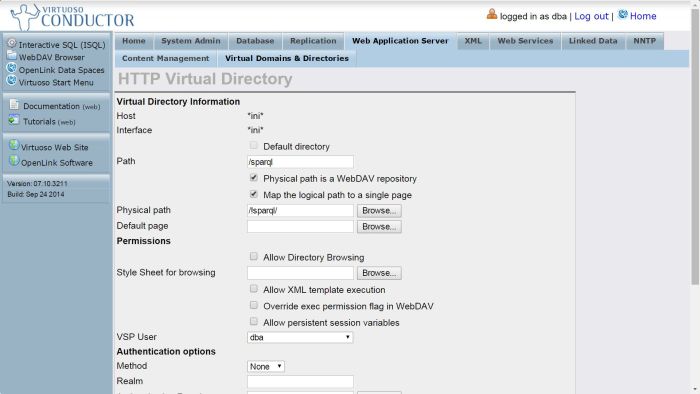
-
The SPARQL endpoint will not be accessible on http://hostname:port/sparql the the newly configured slave nodes:
Figure 2.190. Configure SPARQL Endpoint: SPARQL Endpoint
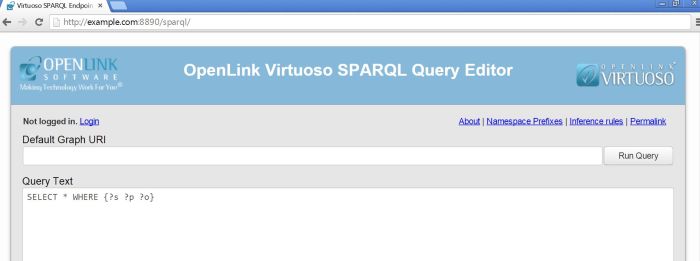
-
Further details on SPARQL endpoint configuration can be found in Service Endpoint documentation section.
-
Typical Virtuoso server log output from a slave node when started, showing the HTTP server running on port 8890, being:
20:12:49 OpenLink Virtuoso Universal Server 20:12:49 Version 07.10.3209-pthreads for Linux as of Apr 26 2014 20:12:49 uses parts of OpenSSL, PCRE, Html Tidy 20:12:49 Registered to OpenLink Virtuoso (Internal Use) 20:12:49 Personal Edition license for 500 connections 20:12:49 Issued by OpenLink Software 20:12:49 This license will expire on Sun May 17 06:18:35 2015 GMT 20:12:49 Enabled Cluster Extension 20:12:49 Enabled Column Store Extension 20:12:57 Database version 3126 20:12:57 SQL Optimizer enabled (max 1000 layouts) 20:12:58 Compiler unit is timed at 0.000208 msec 20:12:58 Roll forward started 20:12:58 Roll forward complete 20:12:59 Checkpoint started 20:12:59 Checkpoint finished, log reused 20:12:59 HTTP/WebDAV server online at 8890 20:12:59 Server online at 12202 (pid 15969)
Configure load balancing
Step 3 : Configure load balancing
A reverse-proxy service (like Nginx or Apache) can then be configured such that requests are proxied across as any or all nodes of the cluster, to provide the desired load balancing.
Additional Information
-
Only the Primary Node of an Elastic Cluster may be configured as a Publisher for Virtuoso Replication Cluster purposes.
-
The Virtuoso 500 billion triple Berlin SPARQL Benchmark (BSBM) dataset runs were performed on a 24-node Elastic Cluster. Each node was configured to provide HTTP services and a SPARQL endpoint, and the query load was spread over the entire cluster.
